The NEET 2026 Exam is expected to be conducted by the National Testing Agency at various exam centers in May 2026. All the aspirants who are looking forward to appearing for the national level medical examination need to complete their preparations for the exam by studying all the important topics mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026.
Among the NEET Physics Syllabus 2026, Gravitation is among one of the most important chapter that students need to study in order to complete their preparations for the exam. Scroll down in the article below for the NEET Physics MCQs for Gravitation Chapter and access the previous year’s MCQs.
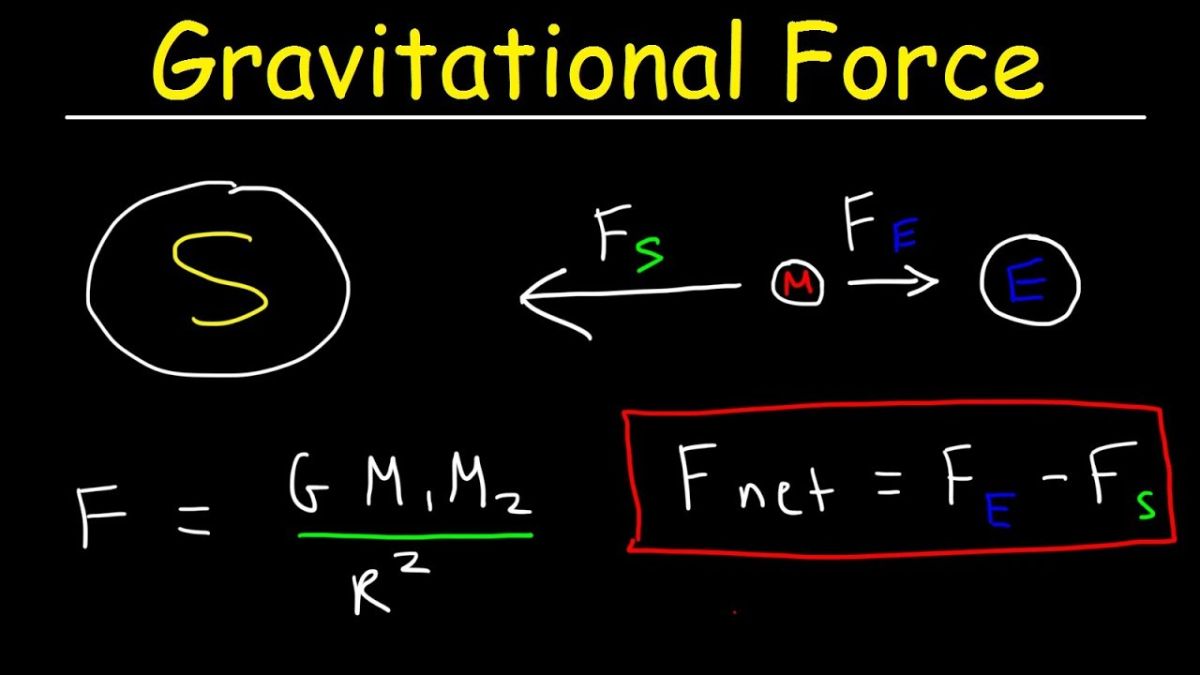
NEET Physics MCQs for Gravitation Chapter
The Gravitation chapter in Physics is a fundamental part of the NEET syllabus. It introduces students to the concepts of gravitational force, laws of motion, and planetary motion, all of which are crucial for understanding various phenomena in nature. Mastery of this chapter is essential for aspiring medical students, as it not only forms the basis of many questions in the NEET exam but also builds the foundation for other chapters in Physics.
In this article, we will dive into some of the most important Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) from the Gravitation chapter. This guide will help you not only prepare effectively for the exam but also strengthen your understanding of the topic.
Key Concepts in Gravitation
The Gravitation chapter in the NEET Physics section is one of the most important chapter that students need to study in process to complete their preparations. NEET Physics Gravitation chapter MCQs focus on understanding the universal law of gravitation, Kepler’s laws, acceleration due to gravity and its variation, gravitational potential energy, and the dynamics of satellites, including escape velocity, orbital velocity, and geostationary satellites. Before diving into the MCQs, let’s quickly revisit the important concepts in the Gravitation chapter:
- Newton’s Law of Gravitation:
This law states that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. - Gravitational Constant (G):
The gravitational constant is a universal constant that appears in the law of gravitation. Its value is approximately.
- Gravitational Potential Energy:
The potential energy due to gravitational force is the energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field. It is given by the formula, where
is the gravitational constant,
and
are the masses of two bodies, and
is the distance between them.
- Escape Velocity:
The escape velocity is the minimum velocity needed by an object to break free from the gravitational pull of the Earth (or any celestial body). It can be calculated using the formula.
- Orbital Motion and Kepler’s Laws:
Kepler’s Laws describe the motion of planets in their orbits. These laws are crucial to understanding the relationship between the masses of celestial bodies and their gravitational forces.
NEET Physics MCQs on Gravitation
Ahead, we have added some of the NEET Physics MCQs from Gravitation Chapter so that all the students appearing for the exam can check and complete their preparations for the same using them. Scroll down in the article below to check the NEET Physics MCQs on Gravitation:
Question 1: What is the value of the gravitational constant
?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Answer: a)
Explanation: The gravitational constant is a fundamental constant of nature and has a fixed value of
, which is crucial for calculating gravitational forces between two masses.
Question 2: The escape velocity from the surface of Earth is approximately:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Answer: a)
Explanation: The escape velocity from the Earth’s surface is calculated using the formula
. The value is approximately
, which is the minimum speed an object must have to escape the Earth’s gravitational pull without further propulsion.
Question 3: The force of attraction between two masses is 50 N when the distance between them is 1 meter. What will be the force when the distance is reduced to 0.5 meters?
a) 100 N
b) 200 N
c) 25 N
d) 50 N
Answer: b) 200 N
Explanation: According to Newton’s Law of Gravitation, the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two masses. If the distance is reduced to half, the force will increase by a factor of 4 (since
). Therefore, the new force is
.
Question 4: Which of the following statements is true about the gravitational potential energy of two masses
and
?
a) The gravitational potential energy is positive for all pairs of masses.
b) The gravitational potential energy is negative for all pairs of masses.
c) The gravitational potential energy is always zero.
d) The gravitational potential energy can be positive or negative depending on the position of the masses.
Answer: b) The gravitational potential energy is negative for all pairs of masses.
Explanation: The gravitational potential energy between two masses is always negative, as it is defined as
, where
is the distance between the masses. The negative sign indicates that the gravitational force is attractive and the system of masses is bound together.
Question 5: Which of the following is not a consequence of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion?
a) The square of the period of revolution of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit.
b) The orbital period of a planet increases as the distance from the sun increases.
c) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus.
d) The planets sweep equal areas in equal times.
Answer: c) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus.
Explanation: This statement refers to Kepler’s first law, not the third law. Kepler’s third law relates to the relationship between the orbital period and the size of the orbit.
Question 6. What happens to the gravitational potential at the centre of the uniform spherical shell which shrinks gradually?
- Remains constant
- Decreases
- Increases
- Oscillates
Answer: (b) Decreases
Question 7. Choose the factor on which the orbital velocity does not depend when the satellite is orbiting close to the earth’s surface
- The mass of the earth
- The mass of the satellite
- The orbital radius
- The radius of the earth
Answer: (b) The mass of the satellite
Question 8. The atmosphere around the earth is held by
- Gravity
- Winds
- Clouds
- None of the above
Answer: (a) Gravity
Tips for Preparing for Gravitation MCQs
Studying and preparing for the NEET Exam requires sheer dedication and understanding of the topics; hence, aspirants need to study the Gravitation chapter carefully. Here are
- Understand the Formulas: The Gravitation chapter is filled with formulas. Understanding when and how to use them is crucial for solving MCQs accurately.
- Conceptual Clarity: It’s not just about memorizing formulas. Grasping the underlying concepts of gravitational force, potential energy, escape velocity, and planetary motion will make solving the questions much easier.
- Practice Previous Year Questions: NEET often repeats similar questions or tests the same concepts in different ways. Practicing past MCQs will help you identify recurring themes and prepare efficiently.
- Use Diagrams: Diagrams can make it easier to visualize concepts like gravitational potential energy, escape velocity, and orbital motion. Ensure you practice interpreting these diagrams in MCQs.
- Time Management: In the exam, time is a precious commodity. Practice solving questions in a time-bound manner to improve speed without compromising accuracy.
Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Gravitation Chapter
In the table listed below, we have added the year wise NEET Physics MCQs for Gravitation Chapter so that all the students can start preparing accordingly. Click on the links below:
| Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Gravitation Chapter | |
| Year | Links |
| 2014 | Click Here |
| 2015 | Click Here |
| 2016 | Click Here |
| 2017 | Click Here |
| 2018 | Click Here |
| NEET Physics Chapters | MCQ Link |
|---|---|
| Physics and Measurement | Click Here |
| Kinematics | Click Here |
| Laws of Motion | Click Here |
| Work, Energy, and Power | Click Here |
| Rotational Motion | Click Here |
| Gravitation | Click Here |
| Properties of Solids and Liquids | Click Here |
| Thermodynamics | Click Here |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | Click Here |
| Oscillation and Waves | Click Here |
| Electrostatics | Click Here |
| Current Electricity | Click Here |
| Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Click Here |
| Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Click Here |









 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








