The preparation phase for the NEET 2026 is going on and all the aspirants who are looking forward to appear for the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for admission into medical courses like MBBS and BDS must start preparing for the exam by reading all the topics mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026.
The NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 contains a very important chapter named Structural Organisation in Animals. Therefore, to help aspirants complete their preparations for the exam, we have added the Structural Organisation in Animals NEET Notes in the article below. Scroll down in the article and check the notes.
Structural Organisation in Animals
“Structural Organisation in Animals” for the NEET exam covers the hierarchical arrangement of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems in multicellular animals, focusing on the four main tissue types (epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous). The chapter details specific examples of these tissues, including simple and compound epithelia, loose and dense connective tissues, skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, and nerve tissues. It also includes the detailed study of the anatomy and physiology of specific organisms like the cockroach, earthworm, and frog to illustrate these concepts.
Levels of Structural Organisation in Animals
The “Levels of Structural Organisation in Animals” describes the biological hierarchy of increasing complexity, where smaller, simpler units combine to form larger, more complex structures. This is essential for the division of labor and efficient functioning in multicellular organisms.
- Cellular Level
- The basic unit of life is the cell.
- Some organisms (e.g., Porifera) show a cellular level of organisation where cells perform different functions but are not organised into tissues.
- Tissue Level
- Found in Coelenterates (Cnidarians) like Hydra.
- Cells performing similar functions are grouped into tissues, leading to better efficiency.
- Organ Level
- Present in Platyhelminthes and higher groups.
- Different tissues combine to form organs that perform specific functions (e.g., flame cells for excretion).
- Organ System Level
- Found in complex animals like annelids, arthropods, molluscs, and vertebrates.
- Organs form well-defined systems (digestive, circulatory, nervous, reproductive).
Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are groups of structurally and functionally similar cells, along with intercellular substances, that work together to perform a specific function. All complex animals are composed of four primary types of tissues: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, and Neural tissue. Animal tissues are broadly classified into four major types, each with subtypes and specialised functions:
1. Epithelial Tissue
- Covers body surfaces and lines internal organs.
- Functions: protection, absorption, secretion, sensory reception.
- Subtypes:
- Simple epithelium – squamous, cuboidal, columnar, ciliated.
- Compound epithelium – multiple layers, for protection (e.g., skin).
2. Connective Tissue
- Connects, supports, and binds body structures.
- Components: cells, fibres (collagen, elastin), and matrix.
- Types:
- Loose connective tissue – areolar, adipose.
- Dense connective tissue – tendons, ligaments.
- Skeletal connective tissue – cartilage, bone.
- Fluid connective tissue – blood, lymph.
3. Muscular Tissue
- Responsible for movement.
- Types:
- Skeletal muscle – voluntary, striated.
- Smooth muscle – involuntary, non-striated.
- Cardiac muscle – involuntary, striated, branched.
4. Neural Tissue
- Specialised to transmit messages.
- Composed of neurons and supporting cells (neuroglia).
- Parts of neuron: cell body, axon, dendrites.
Structural Organisation of Earthworm, Cockroach, and Frog
The “Structural Organisation of Earthworm, Cockroach, and Frog” is a comparative study of the morphology (external features) and anatomy (internal structure) of these three diverse animal types, which represent different phyla (Annelida, Arthropoda, and Chordata). NEET exam often asks questions about the anatomy and morphology of three representative organisms:
1. Earthworm (Pheretima Posthuma)
- Body divided into 100–120 segments (metameres).
- Digestive system: complete, with gizzard for grinding food.
- Circulatory system: closed type with blood vessels and hearts.
- Excretory system: nephridia.
- Nervous system: paired ganglia in each segment.
- Hermaphroditic (reproductive system includes testes and ovaries).
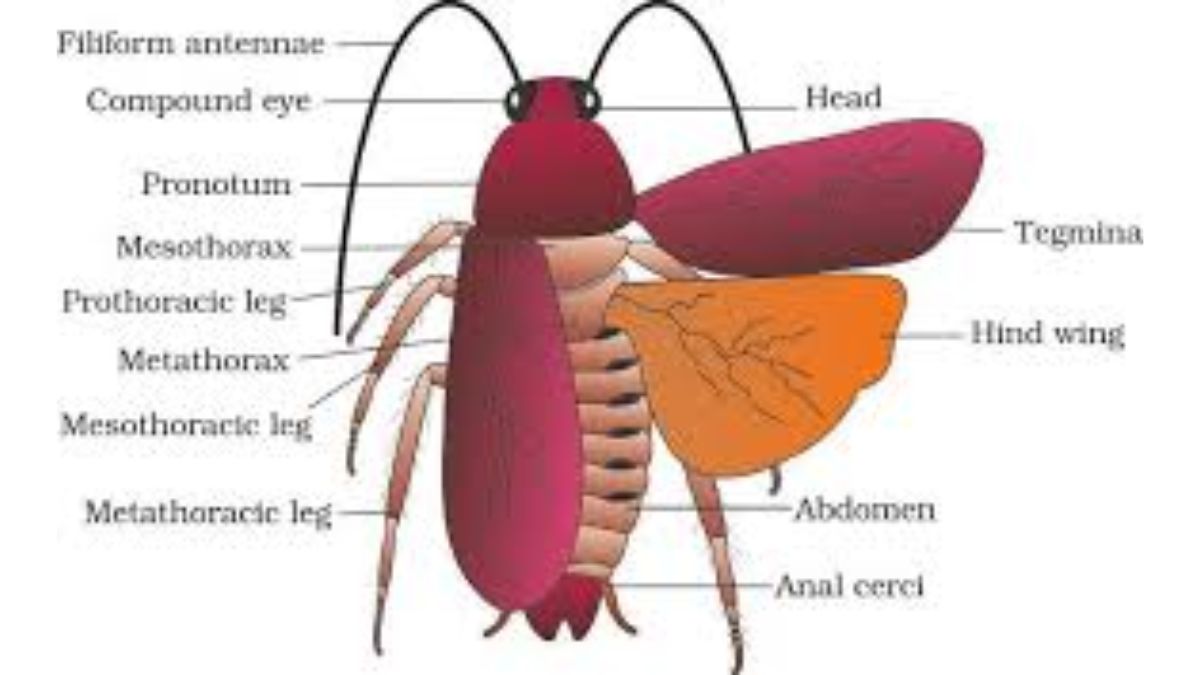
2. Cockroach (Periplaneta Americana)
- Segmented body divided into head, thorax, and abdomen.
- Digestive system: foregut, midgut, hindgut.
- Circulatory system: open type (blood flows in hemocoel).
- Excretion: malpighian tubules.
- Respiratory system: tracheal tubes with spiracles.
- Reproductive system: sexes separate.
3. Frog (Rana Tigrina)
- Amphibian, shows features of both aquatic and terrestrial life.
- Digestive system: stomach, intestine, cloaca.
- Circulatory system: closed with a three-chambered heart.
- Excretion: kidneys and ureters.
- Nervous system: well-developed with brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Separate sexes with external fertilisation.
Importance of Structural Organisation in Animals NEET Notes
Preparing for the Structural Organisation in Animals Chapter require students to use their notes efficiently, therefore, we have listed the importance of Structural Organisation in Animals NEET Notes ahead:
- Understanding tissues and organ systems builds the base for later chapters like digestion, respiration, circulation, and reproduction.
- Questions from this chapter frequently appear in NEET, especially from tissues and representative organisms (earthworm, cockroach, frog).
- Learning about tissues, their types, and functions helps students easily relate structure with function in animals.
- Notes highlight differences and similarities among earthworm, cockroach, and frog, which are crucial for solving application-based questions.
- Well-structured notes allow quick last-minute revision of key points, diagrams, and definitions before exams.
- NEET often includes diagram-based questions from tissues and organs; these notes consolidate all diagrams in one place for easy recall.
NEET Important Question – Structural Organisation in Animals
Question 1. Which connective tissue connects muscles to bones?
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Cartilage
- Areolar
Answer: b) Tendons
Question 2. Identify the tissue responsible for movement in the gut.
- Skeletal muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Areolar tissue
Answer: b) Smooth muscle
Question 3. Which part of the neuron carries impulses away from the cell body?
- Dendrite
- Axon
- Nissl’s granules
- Neuroglia
Answer: b) Axon
Question 4. In cockroach, blood does not transport:
- Nutrients
- Hormones
- Oxygen
- Excretory products
Answer: c) Oxygen
Question 5. Earthworm respires through:
- Skin
- Gills
- Trachea
- Book lungs
Answer: a) Skin
Question 6. Assertion (A): Cuboidal epithelium is found in kidney tubules.
Reason (R): It provides mechanical support and helps in absorption and secretion.
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, R is false
- A is false, R is true
Answer: a)
Question 7. Assertion (A): Frog has a three-chambered heart.
Reason (R): It has two auricles and one ventricle that allow complete separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation
- Both A and R are true, but R is not correct explanation
- A is true, R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: c)
Question 8. Identify the tissue shown in the diagram with multinucleated cylindrical fibres.
- Smooth muscle
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Cuboidal epithelium
Answer: b) Skeletal muscle
Question 9. The given diagram shows a neuron. Which part receives impulses?
- Axon terminal
- Dendrites
- Node of Ranvier
- Axoplasm
Answer: b) Dendrites
Question 10. In earthworm, which segment contains the clitellum?
- 1st–5th
- 13th–17th
- 19th–25th
- 30th–40th
Answer: b) 13th–17th
Question 11. Which type of epithelial tissue lines the kidney tubules?
- Squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Ciliated epithelium
Answer: b) Cuboidal epithelium
Question 12. Identify the connective tissue that stores fat.
- Areolar
- Adipose
- Ligament
- Cartilage
Answer: b) Adipose
Question 13. What type of circulatory system is present in earthworm?
- Open
- Closed
- Lymphatic
- None
Answer: b) Closed
Question 14. The excretory organs of cockroach are:
- Nephridia
- Malpighian tubules
- Kidneys
- Flame cells
Answer: b) Malpighian tubules
Question 15. Which chambered heart is found in frog?
- Two-chambered
- Three-chambered
- Four-chambered
- None of the above
Answer: b) Three-chambered










 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








