The National Testing Agency will be conducting the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for admission into medical courses like MBBS and BDS for the academic session 2026-27 at various examination centers in May 2026. All the students with aspirations of a successful career in the medical field must start preparing by reading and learning all the topics mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026. One of the important topics covered in the NEET Biology Syllabus 2026 is the Reproductive Health. Therefore, in this article, we have shared the NEET Notes for the Reproductive Health chapter that not only guides students through their preparation phase but will also share the important questions.
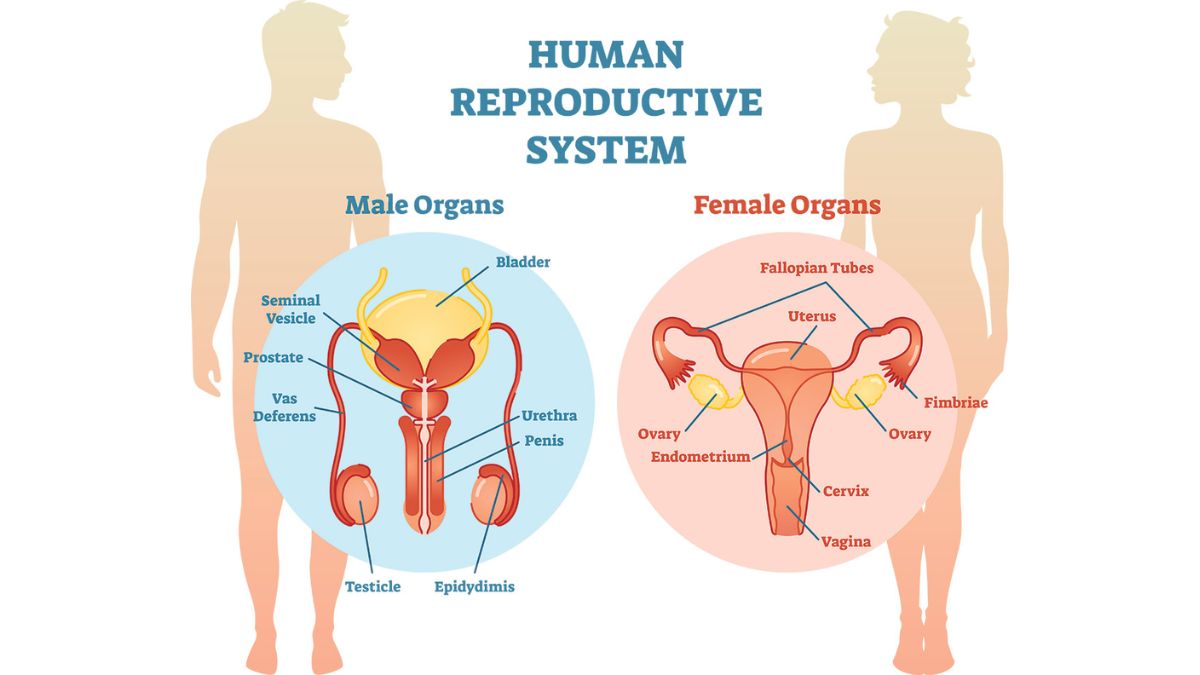
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health is a state of total physical, mental, and social well-being regarding all aspects of the reproductive system, not just the absence of disease. It includes having a safe and satisfying sex life, the ability to reproduce and make informed choices about when and how often to do so, and freedom from coercion and violence. Key components include access to contraception and family planning, maternal and child health services, prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and broader societal support through education and healthcare.
Components of Reproductive Health
Reproductive health consists of the following major components:
- Sexual Health – Maintenance of physical, emotional, and social well-being in relation to sexuality.
- Maternal Health – Care provided to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum period.
- Family Planning – Regulating reproduction through birth control methods and planned parenthood.
- Prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) – Awareness and treatment of diseases like HIV, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis.
- Awareness and Education – Spreading knowledge about reproductive processes, hygiene, and responsible behavior.
Governmental and Non-Governmental Initiatives
To improve reproductive health, several initiatives have been taken at the national and international levels:
- Family Planning Programme (1951) – India was the first country to start a national family planning program.
- Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Programme – Introduced to provide maternal and child health care.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) – Promotes institutional deliveries to reduce maternal mortality.
- National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) – Prevents and controls the spread of HIV/AIDS.
- NGO Initiatives – Organizations like MAMTA and FPAI work toward reproductive awareness and education.
Population Explosion and Control
“Population explosion” refers to the rapid and excessive increase in human numbers, while “population control” includes the efforts and policies to manage this growth through strategies like family planning, education, and empowerment. The explosion is caused by a high birth rate exceeding the death rate, leading to issues like overpopulation, resource depletion, poverty, and environmental damage. Control measures aim to mitigate these effects by influencing birth rates and promoting sustainable development.
Population Explosion
An exponential increase in population due to the high birth rate and low death rate is known as a population explosion. It can lead to resource scarcity, unemployment, and environmental imbalance.
Causes:
- Improved medical facilities and lower death rates
- Lack of awareness about contraception
- Early marriages and lack of family planning
Control Measures:
- Use of contraceptives
- Awareness campaigns
- Incentives for smaller families
- Compulsory education and employment for women
Methods of Birth Control (Contraception)
Contraceptive methods help regulate pregnancy and control population growth. They are divided into several types:
1. Natural Methods
These methods avoid sexual intercourse during the fertile period.
- Periodic Abstinence – Avoiding intercourse during ovulation.
- Coitus Interruptus – Withdrawal before ejaculation.
- Lactational Amenorrhea – Temporary infertility during breastfeeding.
2. Barrier Methods
Physical barriers prevent sperm from reaching the ovum.
-
Condoms, Diaphragms, Cervical caps, Vaults
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Inserted into the uterus to prevent fertilization.
-
Examples: Copper-T, Multiload 375, LNG-20
4. Oral Contraceptives
Hormonal pills that prevent ovulation.
-
Examples: Mala-D, Saheli
5. Surgical Methods (Sterilization)
Permanent methods of birth control.
- Vasectomy (in males)
- Tubectomy (in females)
Infertility and Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Infertility is the inability to conceive even after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse.
Causes:
- Physical, hormonal, or psychological issues
- Genetic disorders
- Blockages in reproductive tracts
ART Techniques:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) – Fertilization outside the body followed by embryo transfer (test-tube baby).
- Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) – Zygote placed in fallopian tube.
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) – Transfer of gametes into the fallopian tube.
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) – Direct injection of sperm into the ovum.
- Artificial Insemination (AI) – Insertion of semen into the female reproductive tract.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
STDs are infections transmitted through sexual contact.
Common STDs:
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Genital herpes
- Hepatitis-B
- HIV-AIDS
Prevention:
- Avoid multiple sexual partners
- Use condoms
- Regular medical check-ups
- Education and awareness
Adolescent Health and Education
Adolescents should be provided with correct information regarding puberty, menstruation, sexual behavior, and hygiene. Sex education in schools promotes:
- Awareness about reproductive organs and functions
- Prevention of STDs
- Healthy attitude toward sexuality
- Reduction in teenage pregnancies
Importance of Reproductive Health
Reproductive health plays a very vital role in maintaining the population stability across the society. Here, we have cited some pointers explaining the importance of Reproductive health:
- Promotes family planning and helps in controlling population growth.
- Prevents reproductive disorders and infections through awareness and early diagnosis.
- Reduces maternal and infant mortality rates by ensuring safe pregnancies and deliveries.
- Prevents sexually transmitted infections (STIs) through education and preventive measures.
- Improves fertility health and assists couples facing infertility.
- Ensures gender equality by empowering women with reproductive rights and awareness.
- Encourages responsible sexual behavior and emotional maturity among adolescents.
NEET Important Questions – Reproductive Health
Queston 1. What are the objectives of the RCH Programme?
Question 2. Explain the different methods of contraception.
Question 3. Define infertility and describe ART techniques.
Question 4. What are the causes and preventive measures of population explosion?
Question 5. List the major STDs and their preventive measures.
Question 6. What is the importance of reproductive health in adolescents?
Question 7. Differentiate between vasectomy and tubectomy.
Question 8. Write a note on the role of government programs in reproductive health.








 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...









