The Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism is a very important chapter in the Physics textbook of class 12th. One of the important aspects of this chapter is that it is covered in the NEET Physics Syllabus as well as the JEE Main Physics Syllabus. Therefore, all the aspirants who are looking forward to appear in either of the exams must try to understand all the concepts and complete their preparations for the same.
In this article, we have shared the NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter so that all the aspirants for this NEET 2026 exam can complete their preparations and build a strong understanding of the key topics from this chapter.
NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter
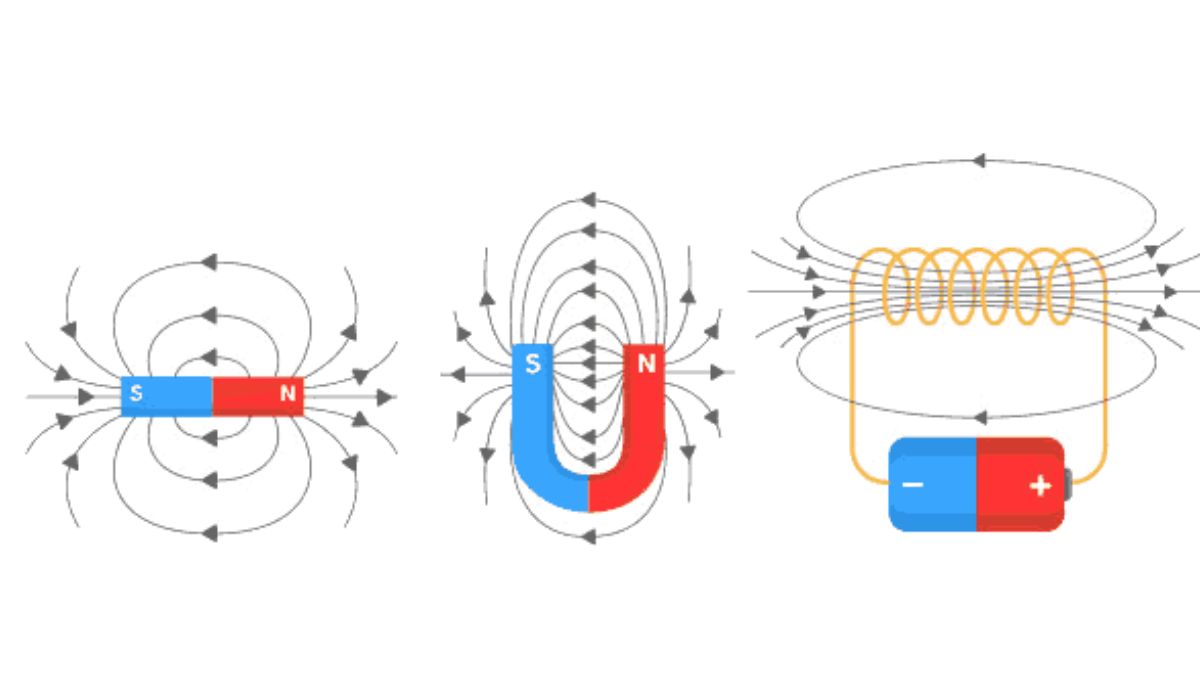
The chapter on the Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism explores the fundamental principle that an electric current produces a magnetic field, first discovered by Hans Christian Oersted, a phenomenon known as electromagnetism. Key concepts include magnetic field lines, which visualize the invisible force field around magnets and current-carrying conductors, and laws like Ampere’s Circuital Law and the Biot-Savart Law, used to calculate the strength and direction of these fields. The chapter also covers the magnetic effects of current in a solenoid, forming an electromagnet, and the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field, often determined by Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Important Topics in Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Preparing for any examination or any important topic/ chapter requires students to give their best. Before appearing for the NEET MCQs of Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter, the aspirants must try to read and learn all the important topics mentioned below:
- Oersted’s Experiment: Understanding how current creates a magnetic field.
- Biot–Savart Law: Formula, direction of magnetic field, and applications.
- Ampere’s Circuital Law: Calculation of magnetic fields in solenoids and toroids.
- Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge: Lorentz force and its applications.
- Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor: Force between parallel conductors.
- Torque on a Current Loop: Magnetic dipole moment, its derivation, and applications.
- Moving Coil Galvanometer: Construction, working principle, and conversion to ammeter/voltmeter.
- Cyclotron: Principle, construction, and limitations.
- Earth’s Magnetism: Magnetic declination, dip, and horizontal component.
- Magnetization & Magnetic Properties of Materials: Dia-, para-, and ferromagnetism.
Importance of Solving NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter
The Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism chapter is one of the most crucial parts of NEET Physics. It deals with the fascinating relationship between electricity and magnetism and how current-carrying conductors produce magnetic fields. For NEET aspirants, this chapter is extremely important because it covers a significant portion of the syllabus and is a favorite for concept-based and numerical questions. Practicing MCQs is one of the best ways to master this chapter. Here are some of the reasons that make this chapter more important:
- Strengthens Conceptual Understanding – This chapter involves many vector quantities, right-hand rules, and derivations. MCQs test your ability to visualize directions of magnetic fields, forces, and torques, helping you solidify your understanding.
- Improves Speed and Accuracy – Regular MCQ practice enables you to quickly solve questions involving formulas like Biot–Savart Law, Ampere’s Law, and Lorentz force. This is crucial for time management during the NEET exam.
- Exam-Oriented Preparation – NEET frequently asks conceptual and numerical questions from this chapter. Solving previous year questions and topic-wise MCQs ensures you are aligned with the exam pattern.
- Boosts Problem-Solving Skills – Questions often combine multiple concepts, such as forces on charged particles in electric and magnetic fields simultaneously. MCQ practice trains you to tackle such application-based problems with ease.
NEET Physics MCQs on Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter
Below, we have added some of the NEET Physics MCQs on Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter so that all the aspirants who are currently studying this chapter can complete their preparations using them. Check and solve the MCQs listed below:
Question 1. The direction of the magnetic field due to a straight current-carrying conductor is determined by:
A) Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
B) Right-Hand Thumb Rule
C) Maxwell’s Corkscrew Rule
D) Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule
Answer: B
Explanation: Right-hand thumb rule gives the direction of the field around a straight conductor.
Question 2. The unit of magnetic dipole moment is:
A) A·m
B) A·m²
C) Wb·m
D) T·m²
Answer: B
Question 3. A proton moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The path followed is:
A) Straight line
B) Helical
C) Circular
D) Parabolic
Answer: C
Explanation: Lorentz force provides centripetal force → circular motion.
Question 4. A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by connecting:
A) High resistance in series
B) Low resistance in series
C) Low resistance in parallel
D) High resistance in parallel
Answer: C
Question 5. The torque acting on a magnetic dipole of moment M in a magnetic field B is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
Answer: C
Question 6. The SI unit of magnetic field is:
A) Weber
B) Gauss
C) Tesla
D) Henry
Answer: C
Question 7. The magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying circular arc of angle θ is proportional to:
A) θ
B) sinθ
C) cosθ
D) tanθ
Answer: A
Question 8. The magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance is:
A) Positive and large
B) Positive and small
C) Negative
D) Infinite
Answer: C
Question 9. The force on a charge moving parallel to magnetic field lines is:
A) Maximum
B) Minimum but not zero
C) Zero
D) Can’t be predicted
Answer: C
Question 10. The direction of force on a current-carrying conductor placed in magnetic field is given by:
A) Right-hand thumb rule
B) Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
C) Ampere’s Rule
D) Faraday’s Law
Answer: B
Question 11. The north pole of a magnetic needle freely suspended points towards:
A) Magnetic North Pole of Earth
B) Magnetic South Pole of Earth
C) Geographic South Pole
D) Geographic Equator
Answer: B
Explanation: Magnetic north pole is attracted to Earth’s magnetic south pole near geographic north.
Question 12. In a cyclotron, the radius of the particle’s path is directly proportional to:
A) Velocity
B) Magnetic field
C) Mass of particle
D) Charge
Answer: A
Question 13. The magnetic field inside a toroid is:
A) Uniform
B) Zero
C) Maximum near the outer edge
D) Maximum near the inner edge
Answer: A
Question 14. Magnetic field lines:
A) Intersect each other
B) Do not intersect
C) Are infinite straight lines
D) Are imaginary only
Answer: B
Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter
In the table listed below, we have added the year wise NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter so that all the students can start preparing accordingly. Click on the links below:
| Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism Chapter | |
| Year | Links |
| 2014 | Click Here |
| 2015 | Click Here |
| 2016 | Click Here |
| 2017 | Click Here |
| 2018 | Click Here |
| NEET Physics Chapters | MCQ Link |
|---|---|
| Physics and Measurement | Click Here |
| Kinematics | Click Here |
| Laws of Motion | Click Here |
| Work, Energy, and Power | Click Here |
| Rotational Motion | Click Here |
| Gravitation | Click Here |
| Properties of Solids and Liquids | Click Here |
| Thermodynamics | Click Here |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | Click Here |
| Oscillation and Waves | Click Here |
| Electrostatics | Click Here |
| Current Electricity | Click Here |
| Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Click Here |
| Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Click Here |









 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








