The preparation phase for the NEET 2026 exam is on. All the students who are in their class 12th or are preparing for the exam must now start reading about all the chapters and topics mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026. Physics, being one of the most prominent and important part of the NEET Exam requires sheer dedication and attention from the aspirants. Therefore, in this series of NEET Physics MCQs, we have got the NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices Chapter in the article below so that all the aspirants studying this chapter can complete their preparations for the chapter by solving more and more MCQs.
NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices Chapter
An “Electronic Devices” chapter typically covers fundamental components like semiconductors, diodes, and transistors, explaining their internal mechanisms and how they are used for functions such as signal amplification and switching. Key topics often include the energy band theory of solids, PN-junctions, the operation and characteristics of diodes like Zener diodes and LEDs, different types of transistors (BJTs, FETs), and basic logic gates. The chapter also introduces the concepts of analog and digital signals and may touch on their practical applications in circuits.
Important Topics in Electronic Devices for NEET
Electronic Devices is a scoring chapter in NEET Physics that deals with the behavior and application of semiconductors, diodes, transistors, and logic gates. Questions from this chapter are usually straightforward, formula-based, and require conceptual clarity. Regular practice of NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices will help you master this chapter, improve problem-solving speed, and secure easy marks in the exam. Before solving MCQs, focus on understanding these key concepts from NCERT:
- Semiconductors: Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, doping, carrier concentration, conductivity.
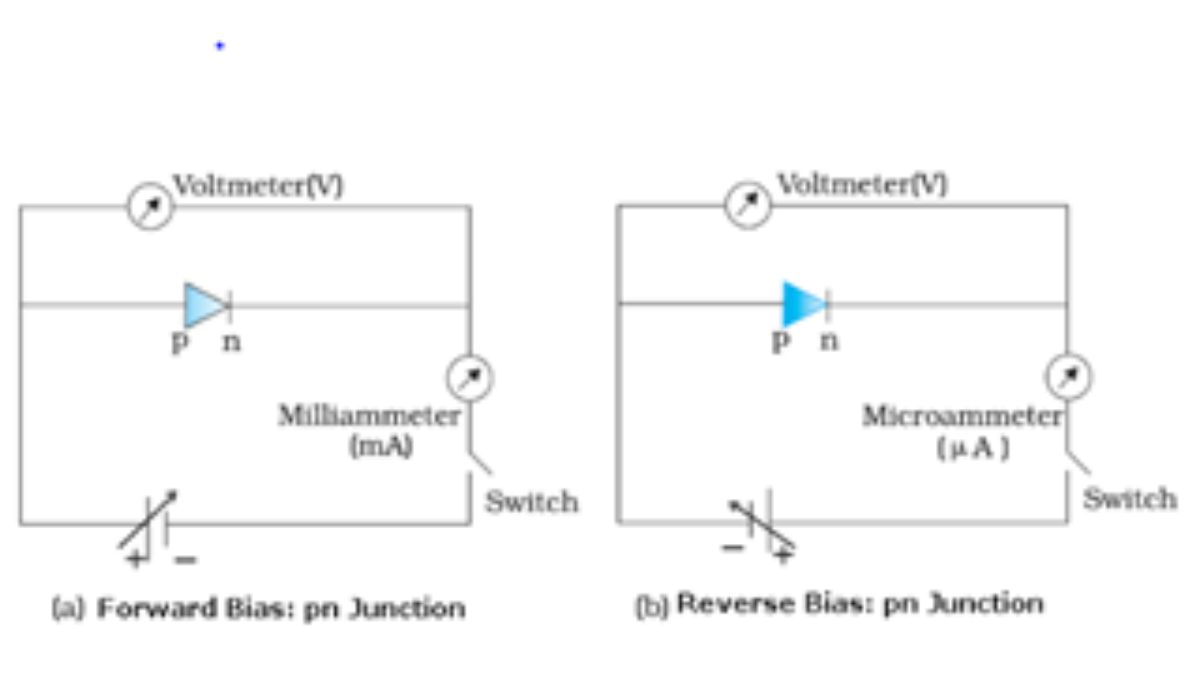
- PN Junction Diode: Characteristics, forward and reverse bias, breakdown voltage.
- Zener Diode: Working and application as a voltage regulator.
- Diode Applications: Rectifiers (half-wave, full-wave), efficiency, ripple factor.
- Transistors: Configuration (CE, CB, CC), current gain, transistor as an amplifier and switch.
- Logic Gates: AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR gates and truth tables.
- Solar Cell, LED, Photodiode: Working principles and applications.
Importance of Solving NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices
The Electronic Devices chapter is an important part of the NEET Physics syllabus, typically accounting for 2-3 questions, which translates to a potential of 8-12 marks. The questions are often conceptual and numerical, requiring a strong grasp of the fundamentals. Practicing MCQs from this chapter helps in:
- Concept Reinforcement: Strengthens your understanding of semiconductor physics and electronic components.
- Quick Problem-Solving: Improves calculation speed for diode currents, transistor currents, and rectifier efficiencies.
- Error Reduction: Helps avoid common mistakes in circuit analysis and logic gate simplifications.
- Exam-Readiness: Most NEET questions are based on standard NCERT concepts – practice ensures familiarity with them.
NEET Physics MCQs on Electronic Devices Chapter
The aspirants who are looking forward to appear for the NEET Exam must start preparing for the exam by solving more and more Electronic Devices MCQs as listed below:
Question 1: In an intrinsic semiconductor, the number of electrons is:
a) Greater than holes
b) Less than holes
c) Equal to holes
d) Zero
Answer: c) Equal to holes
Question 2: When a PN junction is forward biased, the depletion layer:
a) Widens
b) Disappears completely
c) Narrows
d) Remains unchanged
Answer: c) Narrows
Question 3: In a forward-biased diode, current is mainly due to:
a) Majority carriers
b) Minority carriers
c) Drift current
d) Displacement current
Answer: a) Majority carriers
Question 4: The current gain (β) of a transistor in CE configuration is 100. If base current is 40 μA, collector current is:
a) 2 mA
b) 4 mA
c) 0.4 mA
d) 1 mA
Answer: a) 2 mA
Solution:
Question 5: In a transistor, the emitter current is 5 mA and collector current is 4.9 mA. Current gain α (alpha) is:
a) 0.49
b) 0.98
c) 1.02
d) 0.50
Answer: b) 0.98
Solution:
Question 6: In a half-wave rectifier, the maximum efficiency is:
a) 100%
b) 50%
c) 81.2%
d) 40.6%
Answer: d) 40.6%
Question 7: A Zener diode is used as:
a) Current amplifier
b) Voltage regulator
c) Oscillator
d) Rectifier
Answer: b) Voltage regulator
Question 8: The Fermi level in an n-type semiconductor:
a) Moves towards conduction band
b) Moves towards valence band
c) Remains constant
d) Moves to the mid-gap
Answer: a) Moves towards conduction band
Question 9: The current in a forward-biased PN junction diode is of the order of:
a) μA
b) mA
c) nA
d) A
Answer: b) mA
Question 10: The output of a NOT gate is 1 when the input is:
a) 1
b) 0
c) Both 1 and 0
d) None of these
Answer: b) 0
Question 11: The truth table given below represents which logic gate?
| A | B | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
a) NOR Gate
b) NAND Gate
c) AND Gate
d) XOR Gate
Answer: b) NAND Gate
Question 12: The device used for converting solar energy into electrical energy is:
a) LED
b) Photodiode
c) Solar cell
d) Zener diode
Answer: c) Solar cell
Question 13: When a PN junction is reverse biased, current is due to:
a) Majority carriers
b) Minority carriers
c) Both majority and minority carriers
d) Thermal agitation only
Answer: b) Minority carriers
Question 14: In a transistor, the relation between currents is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Answer: c)
Question 15: The ripple factor of a full-wave rectifier is:
a) 1.21
b) 0.482
c) 0.707
d) 0.242
Answer: b) 0.482
Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices Chapter
In the table listed below, we have added the year wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices Chapter so that all the students can start preparing accordingly. Click on the links below:
| Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electronic Devices Chapter | |
| Year | Links |
| 2014 | Click Here |
| 2015 | Click Here |
| 2016 | Click Here |
| 2017 | Click Here |
| 2018 | Click Here |
| NEET Physics Chapters | MCQ Link |
|---|---|
| Physics and Measurement | Click Here |
| Kinematics | Click Here |
| Laws of Motion | Click Here |
| Work, Energy, and Power | Click Here |
| Rotational Motion | Click Here |
| Gravitation | Click Here |
| Properties of Solids and Liquids | Click Here |
| Thermodynamics | Click Here |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | Click Here |
| Oscillation and Waves | Click Here |
| Electrostatics | Click Here |
| Current Electricity | Click Here |
| Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Click Here |
| Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Click Here |









 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








