The National Testing Agency will be conducting the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test in May 2026. This national level examinations is a single window gateway for aspirants looking forward to getting admission in medical courses like MBBS and BDS at top rated medical institutions like AIIMS, JIPMER, etc. To prepare for this exam, aspirants need to study each and every topic mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026. One such chapter mentioned in the NEET Physics Syllabus 2026 is the Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
In this article below, we have shared the NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter so that all the students studying this chapter can complete their preparations and test their understanding of the chapter.
NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter
The chapter on Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) and Alternating Current (AC) explores the generation of voltage and current in conductors due to changing magnetic fields, as described by Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law, and the characteristics of alternating current, which varies in magnitude and direction over time. Key topics include the process of induction (such as in generators and transformers), eddy currents, and the properties of circuits containing resistance, inductance, and capacitance, which determine AC behavior and power delivery.
Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) and Alternating Currents (AC) is one of the most scoring chapters in NEET Physics. It combines concepts of Faraday’s Laws, Lenz’s Law, Eddy Currents, Self & Mutual Induction, and AC circuits (including LCR circuits, resonance, and power factor). A solid understanding of this chapter can help you solve multiple NEET questions quickly and accurately.
Important Topics in NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter
The Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current chapter covers:
- Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction – Induced EMF, flux change, and Lenz’s law
- Motional EMF – Work done in moving conductors, force on conductors
- Self & Mutual Induction – Coefficients of self/mutual inductance, energy stored in an inductor
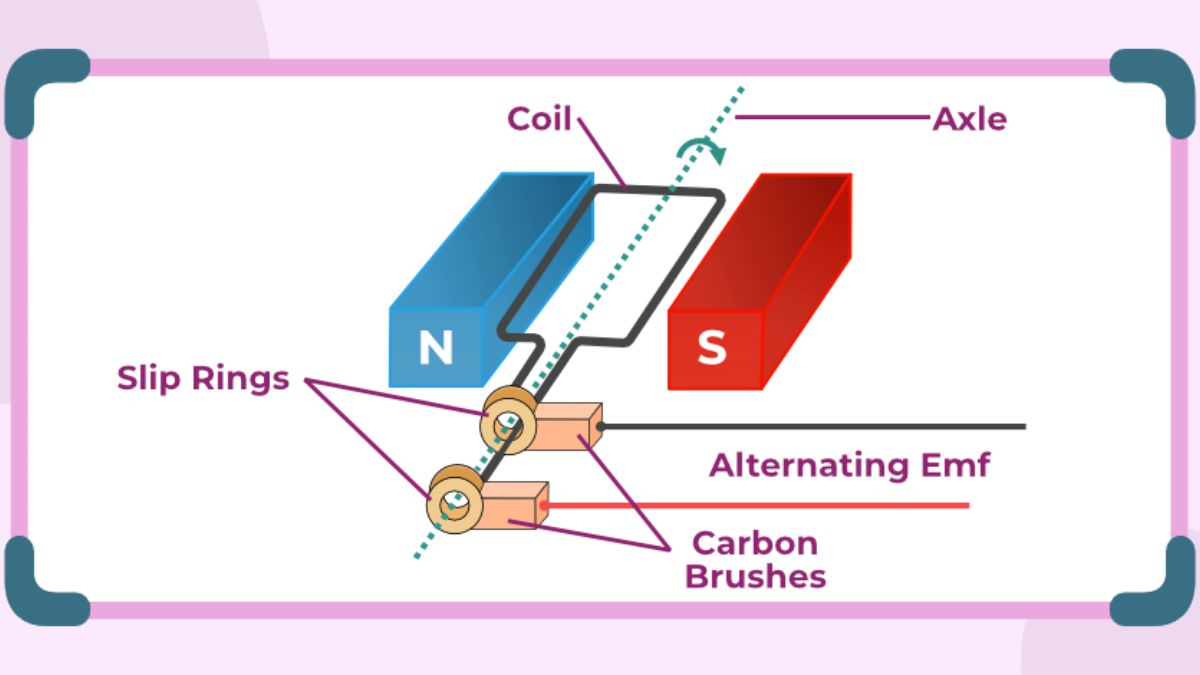
- AC Generator – Working principle and expression for induced emf
- AC Circuits –
- Pure resistive, inductive, and capacitive circuits
- LCR series circuit (phasor diagrams, resonance condition, impedance)
- Power factor and power dissipated in AC circuits
- Transformers – Principle, working, efficiency, energy losses
These topics are application-heavy, making MCQ practice essential to build speed and accuracy.
Importance of Solving NEET Physics MCQs for EMI & AC
The Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents is a very important chapter in class 12th Physics, therefore, preparing best for this chapter requires students to solve as many MCQs as possible. By practicing more and more NEET Physics MCQs for EMI & Ac Chapter, aspirants help themselves in multiple ways like:
- Concept Reinforcement: MCQs check your understanding of Faraday’s law, induced emf, and phase relations in AC circuits.
- Formula Application: Regular practice helps you quickly apply key formulas like
,
, and
.
- Time Management: MCQs boost speed and train you to eliminate incorrect options faster.
- Exam-Oriented Preparation: Many NEET questions are directly based on standard derivations and phasor concepts from this chapter.
- Numerical Accuracy: Solving circuit-based problems improves calculation speed and reduces silly mistakes.
NEET Physics MCQs on Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter
The aspirants who are looking forward to appear for the NEET Exam must start preparing for the exam by solving more and more Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents MCQs as listed below:
Question 1. A conducting loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field
perpendicular to its plane. If the magnetic field decreases at a constant rate, the induced current in the loop will be:
a) Zero
b) Constant
c) Increasing linearly with time
d) Decreasing exponentially with time
Answer: (b) Constant
Explanation:
. Since
is constant, induced emf is constant, hence current is constant.
Question 2. The self-inductance of a coil is
. If the current through the coil changes from 2 A to 6 A in 0.02 s, the magnitude of induced emf is:
a) 200 V
b) 400 V
c) 800 V
d) 1600 V
Answer: (c) 800 V
Solution:
Question 3. In a series LCR circuit at resonance:
a) Current is minimum
b) Impedance is maximum
c) Voltage across L and C are equal and opposite
d) Power factor is zero
Answer: (c) Voltage across L and C are equal and opposite
Explanation: At resonance,
, so voltages across L and C cancel each other. Current is maximum, impedance = R, and power factor = 1.
Question 4. The rms value of an alternating current given by
is:
a) 2.5 A
b) 3.54 A
c) 5 A
d) 7.07 A
Answer: (b) 3.54 A
Solution:
Peak current,
A
Question 5. The efficiency of an ideal transformer is:
a) Zero
b) 100%
c) Less than 50%
d) More than 100%
Answer: (b) 100%
Explanation: For an ideal transformer, there is no energy loss, hence efficiency = 100%.
Question 6. A rectangular coil of N turns and area
is rotated with a constant angular velocity
in a uniform magnetic field
. The maximum emf induced is:
a)
b)
c)
d) Zero
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
(from AC generator principle).
Question 7. An inductor of
carries a current of
. The energy stored in the inductor is:
a) 10 J
b) 25 J
c) 50 J
d) 100 J
Answer: (b) 25 J
Solution:
Question 8. The current leads the voltage by
in:
a) Pure resistor
b) Pure inductor
c) Pure capacitor
d) Series LCR circuit at resonance
Answer: (c) Pure capacitor
Explanation: In a capacitor, current leads voltage by 90°.
Question 9. A coil of resistance
and inductance
is connected to a 12 V DC source. The time constant of the circuit is:
a) 0.01 s
b) 0.1 s
c) 1 s
d) 10 s
Answer: (b) 0.1 s
Solution:
Correct Answer: (a) 0.01 s (Be careful! It is a very common mistake.)
Question 10. In a transformer, if the primary coil has 500 turns and the secondary coil has 1000 turns, then the transformer is:
a) Step-up with voltage doubled
b) Step-down with voltage halved
c) Step-up with voltage halved
d) Step-down with voltage doubled
Answer: (a) Step-up with voltage doubled
Explanation:
Hence, output voltage is doubled (step-up).
Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter
In the table listed below, we have added the year wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter so that all the students can start preparing accordingly. Click on the links below:
| Year Wise NEET Physics MCQs for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Chapter | |
| Year | Links |
| 2014 | Click Here |
| 2015 | Click Here |
| 2016 | Click Here |
| 2017 | Click Here |
| 2018 | Click Here |
| NEET Physics Chapters | MCQ Link |
|---|---|
| Physics and Measurement | Click Here |
| Kinematics | Click Here |
| Laws of Motion | Click Here |
| Work, Energy, and Power | Click Here |
| Rotational Motion | Click Here |
| Gravitation | Click Here |
| Properties of Solids and Liquids | Click Here |
| Thermodynamics | Click Here |
| Kinetic Theory of Gases | Click Here |
| Oscillation and Waves | Click Here |
| Electrostatics | Click Here |
| Current Electricity | Click Here |
| Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Click Here |
| Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Click Here |









 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








