Living World Biology Notes for NEET: Here we are discussing the complete study notes of Biology class 11 chapter 1, this will be very useful for NEET UG exam and Board exams as well. The world around us is full of different kinds of living things, making our planet a wonderful and exciting place to live. There are countless types of organisms, each with unique habitats, behaviors, and ways of living.
Even in the most extreme environments—like freezing mountains, hot deserts, boiling springs, and salty lakes—some special life forms manage to survive. These living beings show how amazing and adaptable life can be, even in the toughest conditions. A variety of relationships are known to occur at the micro level, i.e., cellular level, too. Such molecular interactions occur inside, around, and among the cells, which reveal astonishing facts about life. Therefore, when we want to understand what life is really, we get many aspects of it. But a few among them are mainly understood and well-defined.
Living World Biology Notes for NEET
Biologists study and explain various life-forms from technical They also try to classify living organisms from non-living things based on some important criteria. They have also developed some universal norms and processes that make the study of diverse life-forms easier for us.
What Is Living?
The distinctive characteristics exhibited by living organisms are
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Metabolism and cellular organisation
- Consciousness
Growth
- All living organisms can grow. Increase in mass and increase in the number of individuals are twin characteristics of growth.
- A multicellular organism grows by cell In plants, this growth by cell division occurs continuously throughout their life span.
- In animals, this growth is seen up to a certain age; however, cell division occurs in certain tissues to replace lost cells. Unicellular organisms grow by cell division.
Growth is of two types:
- Intrinsic growth: This growth is from inside of the body of a living being
- Extrinsic growth: This growth is from outside i.e., accumulation of material on anybody surface. Non-living exhibits this type of growth.
Diversity In The Living World
- A large variety of living organisms, such as herbs, shrubs, trees, insects, dogs, birds, cats or other animals and plants, are easily seen around us.
- Also, there are many other organisms which are present around us but we cannot see them with our naked eyes, like viruses, bacteria etc.
- These are visible only under. Although when we consider vast areas like forests, deserts, plateaus etc. we find that the number and kinds of living organisms increase manyfold.
- These different kinds of plants, animals and other organisms are referred to as ‘Biodiversity’ of this earth.
Note – The scientific need for simple, stable and internationally accepted systems for naming the living organisms of the world has generated a process called “Nomenclature“. And, before assigning a specific name to an organism, one should determine or know its kind or features correctly, so that one can identify it in each and every part of the world. This is known as “Identification“.
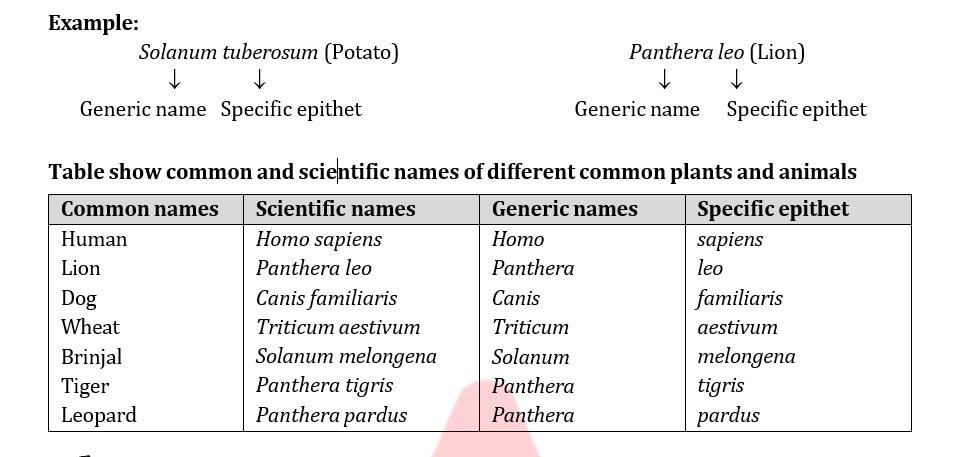
Binomial Nomenclature
All biologists follow internationally agreed and accepted codes of rules or principles while assigning scientific name to known or newly discovered Binomial nomenclature for scientific naming of organisms was developed by Carolus Linnaeus.
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature: Some universal rules of Nomenclature framed under codes of ICZN, ICBN, etc. are as follows:
- Biological names are generally taken from Latin language irrespective of their New names are now derived either from Latin language or Latinised.
- Each organism is given only one name consisting of two The first word in a biological name represents its genus while the second component denotes the specific epithet.
- The scientific name is printed in italics or underlined separately when handwritten to indicate their Latin origin.
- The first word denoting genus starts with a capital letter, while the specific epithet starts with a small
- The name of the author or discoverer is written after specific epithet in abbreviated form. For example, Mangifera indica Linn., it indicates that this species was first described by Linnaeus.
- All the three words (generic name, species epithet and author citation) collectively form binomial epithet.
TAXONOMIC CATEGORIES
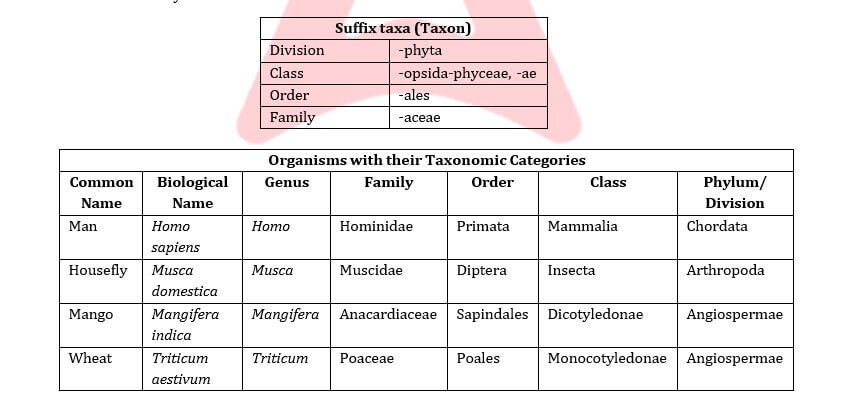
- Classification is not a single-step process but involves a hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category. Since the category is a part of the overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called the taxonomic category and all categories together constitute the taxonomic. Each category, referred to as a unit of classification, in fact, represents a rank and is commonly termed as a taxon (Plural taxa).
- To categorise an individual or group of organisms in a definite rank, we should have all the basic knowledge of its characteristics. This would help us in identifying the similarities and dissimilarities among the individuals of the same kind of organisms, as well as of other kinds of organisms. Here, we will explain all seven broad or obligate categories of taxonomic hierarchy
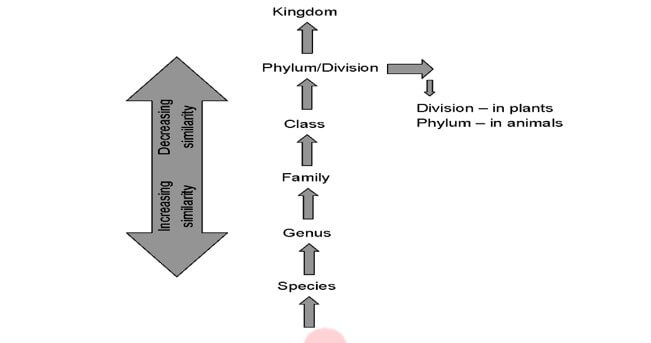
- Species: Species is a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities that show a common set of characters and can be distinguished from other closely related species based on distinct morphological differences.
- :– Mangifera, Solanum and Panthera are genera and represent another higher level of taxon or category.
It is the smallest Taxonomic Category. It is a basic unit of classification.
- Genus: A Genus comprises a group of related species which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera.
e.g. Potato and brinjal are two different species, but both belong to the genus Solanum.
Lion (Panthera leo), Tiger (Panthera tigris), and leopard (Panthera pardus) belong to the same genus –
Panthera
This genus differs from another genus, Felis, which includes cats.
- Family: Family has a group of related genera with still less number of similarities as compared to genus and Families are characterised on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species but reproductive or sexual or floral characters are used mainly.
e.g. Three different genera, Solanum, Petunia and Datura are included in the family Solanaceae.
Among plants, for example, three different genera, Solanum, Petunia and Datura are placed in the family Solanaceae. Among animals for example, genus Panthera, comprising lion, tiger, leopard, is put along
with genus Felis (cats) in the family Felidae. Similarly, if you observe the features of a cat and a dog, you will find some similarities and some differences as well. They are separated into two different families, Felidae and Canidae, respectively.
- Order: Order, being a higher category, is the assemblage of families that exhibit a few similar characters. Generally, orders and other higher taxonomic categories are identified based on the aggregates of e.g. Plant families like Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae are included in the order Polypodiales, which is mainly based on the floral or reproductive or sexual characters.
Ø Animal family Canidae & Felidae are included in order Carnivora
- Class: Class includes organisms of related orders having fewer similarities than
For example, order Primata comprising monkey, gorilla and gibbon is placed in class Mammalia along with the order Carnivora that includes animals like tiger, cat and dog. Class Mammalia has other orders also.
- Phylum or Division: It is a category higher than that of class. The term phylum is used for animals, while division is commonly used for plants. A phylum or division is a group of related classes, i.e., it is formed of one or more classes. Different classes, comprising animals like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, together constitute the next higher category known as “Phylum“. All of these different organisms are placed in the phylum Chordata as all of the animals in these classes have some common characteristics like the presence of a notochord at least at some stage of their lives, a dorsal hollow neural system, etc. In the case of plants, classes with a few similar characters are assigned to a higher category called a division.
- Kingdom: It is the largest taxonomic category based only on a few general characters
- There are 7 main taxonomic They are obligate or essential or broad categories i.e. they are strictly used at the time of any plant classification. There are some extra or sub-categories, like sub-division, sub-order, sub-family, etc. They are used only when they are needed
- The classification of any plant or animal is written in descending or ascending order
- Taxonomic Hierarchy– Descending or ascending arrangement of taxonomic categories is known as hierarchy.
Living World Biology Notes PDF Download with Practice Question
Students can download the full study notes of the Living World chapter for free from the link below. There, you will find many practice questions for each concept for better understanding.
| Living World Biology Notes Pdf Download Class 11 | |
| Living World Biology Notes Pdf Download In English Free | Click Here |









 CUET Arts Syllabus 2026 Out, Download Do...
CUET Arts Syllabus 2026 Out, Download Do...
 CUET PG Admit Card 2026 (Out Soon), Down...
CUET PG Admit Card 2026 (Out Soon), Down...
 CBSE Class 10 Hindi Answer Key 2026 PDF ...
CBSE Class 10 Hindi Answer Key 2026 PDF ...














