The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test is a national level entrance examination conducted by the National Testing Agency at various exam centers across the nation. All the aspirants who are looking forward to appear for the NEET 2026 exam need to complete their preparations for the exam by reading all the topics mentioned in the NEET Syllabus 2026. One of the crucial topics, Excretory Products and Their Elimination, is a crucial topic that should be studied by the students to complete their understanding and achieve high scores in the NEET Exam. Scroll down in the article below to check the Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes listed below in the article.
Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes
The NEET topic “Excretory Products and Their Elimination” covers the process of removing metabolic wastes like urea, carbon dioxide, and excess salts and water from the body to maintain homeostasis. It details the main excretory products, such as urea, CO₂, and uric acid, and explains the vital roles of organs like the kidneys, liver, lungs, and skin in their elimination through urine, exhalation, sweat, and other routes. The topic also discusses different types of excretory products and nitrogenous wastes (ammonia, urea, uric acid) and how different organisms, like aquatic animals and terrestrial mammals, have evolved varying mechanisms to excrete these wastes with different efficiencies in water conservation.
Types of Nitrogenous Waste Products
Different organisms excrete nitrogenous wastes depending on their habitat and evolutionary adaptations:
- Ammonotelic (ammonia excretion)
- Ammonia is highly toxic, soluble in water, and excreted with large amounts of water.
- Found in aquatic animals like bony fishes, amphibians, and invertebrates.
- Ureotelic (urea excretion)
- Urea is less toxic, moderately soluble, and excreted with lesser water.
- Excretory product of mammals, amphibians, and sharks.
- Formed in the liver via the ornithine cycle (urea cycle).
- Uricotelic (uric acid excretion)
- Uric acid is least toxic and excreted as a paste or crystals, conserving water.
- Seen in birds, reptiles, insects, and land snails.
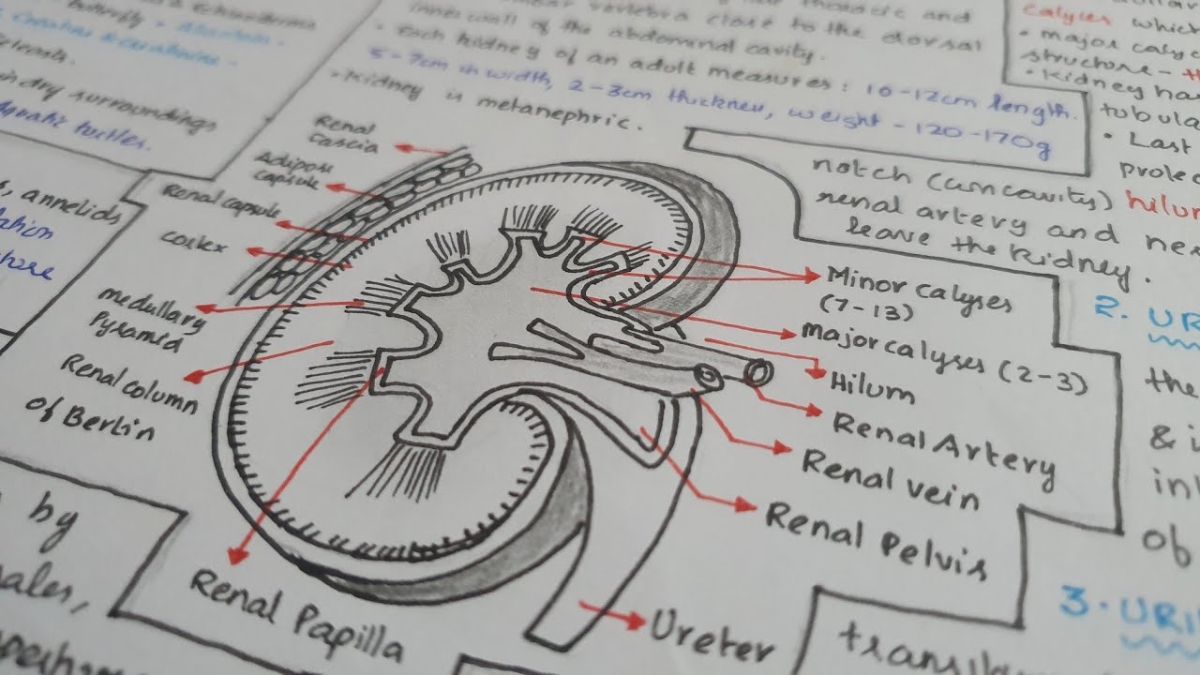
Human Excretory System
1. Kidneys
- Bean-shaped organs located on either side of the vertebral column.
- Functional unit: Nephron.
- Functions:
- Excretion of nitrogenous wastes.
- Osmoregulation (maintaining water and salt balance).
- Acid-base balance.
- Hormone secretion (e.g., renin, erythropoietin).
2. Ureters
- Thin muscular tubes carrying urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder via peristaltic movements.
3. Urinary Bladder
- Hollow muscular organ that stores urine.
- Controlled by the micturition reflex.
4. Urethra
- Tube through which urine is expelled.
External sphincter provides voluntary control over urination.
Structure of a Nephron
Each nephron has two major components:
- Renal Corpuscle
- Bowman’s Capsule: Cup-shaped structure that encloses the glomerulus.
- Glomerulus: Network of capillaries involved in filtration of blood plasma.
- Renal Tubule
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): Reabsorbs nutrients, water, and electrolytes.
- Loop of Henle: Maintains osmotic gradient in the medulla (counter-current mechanism).
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): Involved in selective reabsorption and secretion.
- Collecting Duct: Regulates water reabsorption under the influence of ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
Urine Formation
The process of urine formation occurs in three main steps:
- Glomerular Filtration
- Passive process where blood plasma (except proteins) filters into Bowman’s capsule.
- Filtrate: Water, salts, glucose, amino acids, urea.
- Tubular Reabsorption
- Selective reabsorption of essential substances (like glucose, amino acids, Na⁺, water).
- Mainly in PCT and Loop of Henle.
- Tubular Secretion
- Active transport of substances like H⁺, K⁺, and ammonia into the tubules.
- Helps in maintaining pH and ionic balance.
Regulation of Kidney Function
- ADH (Vasopressin): Increases water reabsorption in collecting ducts.
- Aldosterone: Promotes Na⁺ reabsorption and K⁺ secretion.
- Renin-Angiotensin Mechanism: Regulates blood pressure and GFR (glomerular filtration rate).
- Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF): Lowers blood pressure by promoting Na⁺ excretion.
Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes PDF Download
The students who are appearing for the NEET 2026 exam must start preparing for the Excretory Products and Their Elimination Chapter as it is one of the most important topic to be studied for the exam. To assist students for the final exam we have added the Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes in the article so that they can complete their preparations using it.
Ahead, we have added the direct link to access the Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes PDF. Click on the link and access the PDF.
Weightage of Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes – Last 5 Years
In the table below, we have added the weightage following previous year’s trends along with the NEET Chapter Wise Weightage 2025 for Biology. Check the tables:
| Weightage Following Previous Year’s Trends (2020-2024) | ||||||
| Chapter | Easy | Medium | Hard | Total | Average Q/yr | Weightage |
| Excretory Products and their Elimination | 3 | 5 | 3 | 11 | 2.20 | 4.17% |
| NEET Chapter Wise Weightage 2025 for Biology | |
| Topics | Weightage (%) |
| Excretory Products and their Elimination | 5% |
Importance of Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes
Ahead, we have added some of the pointers that explain the benefits of the Importance of Excretory Products and Their Elimination NEET Notes. Read and check the benefits below:
- High-Weightage Chapter: Frequently asked in NEET Biology with both direct and application-based questions.
- Conceptual Clarity: Builds understanding of nitrogenous wastes, nephron structure, and urine formation processes.
- Physiology Linkage: Connects with other physiology topics like osmoregulation, circulation, and homeostasis.
- Disorders & Clinical Relevance: Covers kidney diseases, dialysis, and transplant concepts often framed in exams.
- Quick Revision Aid: Concise notes help in last-minute preparation and quick recall before exams.
- MCQ Practice Foundation: Simplifies solving numerical and conceptual NEET MCQs on excretion and regulation.
- Scoring Topic: With straightforward facts and diagrams, it helps students secure easy marks in NEET.










 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








