The National Testing Agency will be conducting the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test in May 2026 to short list and admit students for various medical courses like MBBS and BDS. All the students who are to appear in this exam must prepare for each subject and topic using the superior quality notes being shared by the expert faculty team at Adda247. Therefore, in this article, we have shared the Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes that can help students complete preparations for the Chapter 18 of the NEET Biology Syllabus 2026. Scroll down in the article below and download the notes.
Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes
Neural control and coordination is the process by which the nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate and integrate the functions of the body’s organs. The nervous system uses rapid, point-to-point electrical impulses for quick, short-term responses, while the endocrine system relies on slower but more long-lasting chemical signals (hormones) sent through the bloodstream.
The neural system and the endocrine system jointly coordinate and integrate all activities of the organs so that they function in a synchronised fashion. The neural system, built of specialised cells called neurons, provides an organised network of point-to-point connections for rapid coordination.
Structure of Neuron
- Neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
- Parts of a neuron:
- Cell body (Soma/Perikaryon): Contains nucleus, Nissl’s granules, and other organelles.
- Dendrites: Branch-like extensions that receive impulses.
- Axon: Long fiber that transmits impulses away from the cell body.
- Myelin sheath: Provides insulation and increases the speed of impulse conduction.
- Types of neurons:
- Sensory neurons (afferent) – carry signals from receptors to CNS.
- Motor neurons (efferent) – transmit signals from CNS to effectors.
- Interneurons (association neurons) – connect sensory and motor neurons.
Nerve Impulse Conduction
- At rest, the neuronal membrane is polarized due to differential ion concentration (Na⁺ outside, K⁺ inside).
- Resting potential: Approximately –70 mV.
- Depolarization: Na⁺ ions rush inside when threshold is reached, causing the potential to become positive.
- Repolarization: K⁺ ions move out, restoring negativity inside the cell.
- Action potential: The change in polarity across the membrane during impulse conduction.
- Saltatory conduction: In myelinated neurons, impulses jump from one Node of Ranvier to another, making conduction faster.
Synaptic Transmission
- The junction between two neurons is called a synapse.
- Two types of synapses:
- Electrical synapse: Direct flow of ions between neurons; faster.
- Chemical synapse: Most common; neurotransmitters like acetylcholine or dopamine transmit signals.
- Process: Impulse → Ca²⁺ influx → Vesicle fusion → Neurotransmitter release → Binding to receptor → Generation of new action potential.
Human Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into:
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Composed of brain and spinal cord.
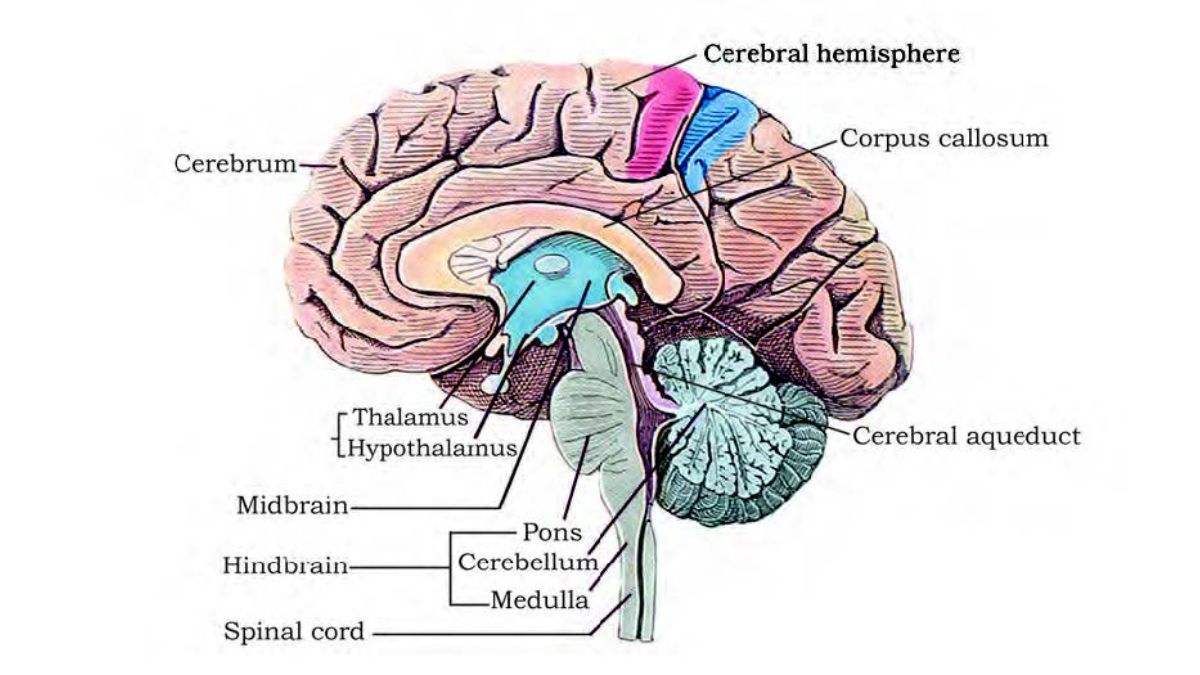
- Brain: Protected by skull, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Forebrain (Cerebrum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus): Higher functions like thinking, emotions, memory.
- Midbrain: Controls reflexes of eyes and ears.
- Hindbrain (Cerebellum, Pons, Medulla): Balance, posture, involuntary activities like respiration and heartbeat.
- Spinal cord: Extends downward from medulla; controls reflexes and conducts messages between body and brain.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
- Divided into:
- Somatic Nervous System: Voluntary control (skeletal muscles).
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Involuntary control (smooth muscles, glands).
- Sympathetic: Prepares body for “fight or flight.”
- Parasympathetic: Restores normal body functions (“rest and digest”).
Reflex Action and Reflex Arc
- Reflex action: Automatic, quick, and involuntary response to stimuli.
- Reflex arc: Pathway of reflex action.
- Components: Receptor → Sensory neuron → CNS → Motor neuron → Effector.
- Examples: Knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal of hand from hot object.
Sense Organs and Neural Coordination
- Eye (Vision):
- Cornea, lens, iris, retina (rods & cones).
- Image formation: Inverted and real on retina.
- Defects: Myopia, hypermetropia, presbyopia, astigmatism.
- Ear (Hearing and Balance):
- Outer ear, middle ear (ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes), inner ear (cochlea, semicircular canals).
- Cochlea – hearing; semicircular canals – balance.
Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes PDF Download
The students who are appearing for the NEET 2026 exam must start preparing for the Neural Control and Coordination Chapter as it is one of the most important topic to be studied for the exam. To assist students for the final exam, we have added the Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes in the article so that they can complete their preparations using it.
Ahead, we have added the direct link to access the Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes PDF. Click on the link and access the PDF.
Importance of Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes
For students appearing for the NEET 2026 Exam we have shared a list pointers that explains the importance of Neural Control and Coordination NEET Notes, check the benfits below:
- Neural control and coordination is a scoring chapter in NEET Biology, and concise notes help students revise quickly before the exam.
- Topics like impulse conduction, synaptic transmission, and brain functions can be tricky—structured notes break them into easy-to-understand points.
- Well-prepared notes include labeled diagrams of neurons, brain, and reflex arcs, which are frequently asked in NEET.
- Notes provide clarity on physiological processes, enabling students to solve NEET’s application and conceptual questions with accuracy.
- During the last phase of preparation, notes act as a quick reference for important definitions, pathways, and examples.
- Notes often include shortcuts, tables, and mnemonics that help in remembering cranial nerves, neurotransmitters, and brain parts.
- With organized content, students can confidently tackle MCQs on reflex actions, sense organs, and neural coordination in the exam.










 NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
NTA NEET 2026 Notification OUT at neet.n...
 NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
NEET Preparation Strategy 2026: Detailed...
 Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...
Free NEET Sample Papers 2026 PDF | Downl...








