The RRB Group D Normalization 2026 process is applied by the Railway Recruitment Boards to ensure fairness in scores when the CBT exam is conducted in multiple shifts. Every year, lakhs of candidates appear for the RRB Group D exam, and because of that, the difficulty level varies from shift to shift. In this article, we have discussed the normalisation process in detail, including the percentile score, the process of normalisation, the calculation of the normalised score, and more.
RRB Group D Normalization 2026
RRB Group D is conducted in multiple shifts because of the huge number of applicants. Some shifts are slightly harder, some are easier. If raw marks are used to prepare merit lists, then candidates from easier shifts get an unfair advantage. To solve this, RRB uses Percentile-based Normalization. According to the official RRB notice, every candidate’s raw score is converted into a Percentile Score, and this percentile becomes the normalized score for result preparation.
RRB Group D Answer Key 2026 Out – Click to Check
What is RRB Group D Normalization?
Normalization is a statistical process that converts raw marks into normalized marks based on the difficulty level of the shift. Instead of comparing how many marks you scored, RRB compares how many candidates you performed better than in your shift by calculating the percentile score. A detailed breakdown of the RRB Group D Normalization process is provided below:
What is Percentile Score?
The percentile score shows the percentage of candidates who scored equal to or less than you in your shift. It is not the same as percentage marks.

For example:
| Candidates in Shift | Your Rank | Percentile |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 200 | 80.00 |
| 1000 | 50 | 95.00 |
| 1000 | 1 (Topper) | 100.00 |
This means you performed better than 80%, 95%, or 100% of candidates in that shift, respectively.
How RRB Uses Percentile for Group D Merit List
Once percentiles are calculated for all shifts:
- All shift percentiles are merged
- These merged percentiles are called RRB Scores
- Merit list is prepared using these scores
If two candidates have the same percentile:
- Older candidate gets higher rank
- If age is same, alphabetical order decides
Base Shift (For Normalization of Marks)
To calculate normalized marks, RRB selects one shift as the Base Shift. The Base Shift becomes the reference scale for everyone. This shift is chosen based on:
- Highest average (mean) marks
- Must have at least 70% of average candidate count
- If tie, shift with highest individual marks wins
- If still tie, shift with highest attendance wins
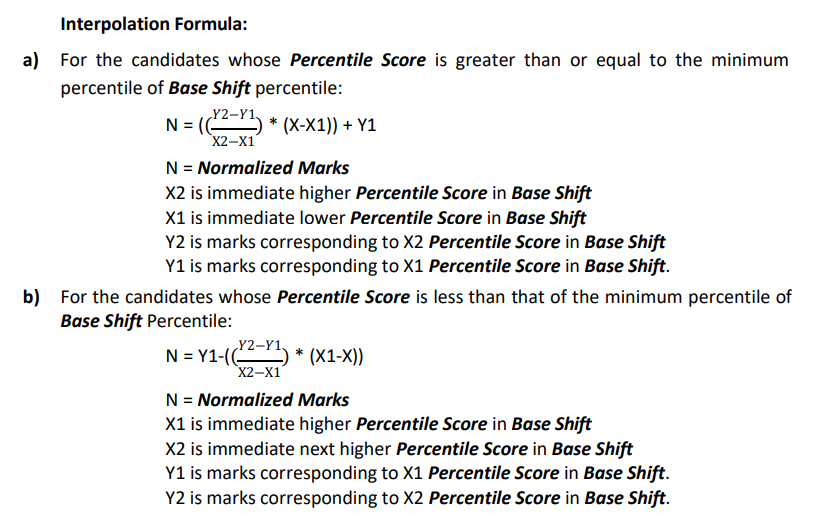
Calculation of Normalised Score
If your percentile belongs to the Base Shift, your normalized marks are taken directly. If not, RRB uses the interpolation formula as per the RRB Group D Normalization:
Minimum Qualifying Marks
RRB Group D Normalization does not remove category-wise eligibility. Candidates must still score the minimum qualifying marks as follows:
| Category | Minimum % |
|---|---|
| UR | 40% |
| EWS | 40% |
| OBC (NCL) | 30% |
| SC | 30% |
| ST | 25% |
| ST (Level-1) | 30% |



 SSC MTS Admit Card 2026 OUT for Re-Exam,...
SSC MTS Admit Card 2026 OUT for Re-Exam,...
 Bihar Jeevika Result 2026 Out Soon @brlp...
Bihar Jeevika Result 2026 Out Soon @brlp...
 CAIIB Exam 2026- Exam Date Out, Apply On...
CAIIB Exam 2026- Exam Date Out, Apply On...

 Adda247 Job portal has complete information about all Sarkari Jobs and Naukri Alerts, its latest recruitment notifications, from all state and national level jobs and their updates.
Adda247 Job portal has complete information about all Sarkari Jobs and Naukri Alerts, its latest recruitment notifications, from all state and national level jobs and their updates.




